
· 1. Particle gradation
The particle gradation of gravel or pebbles should comply with the requirements in the following table:

Stones for concrete should be of continuous grain size. Single-grain fractions should be combined into continuous granular fractions that meet the requirements, and can also be mixed with continuous granular fractions to improve their gradation or form continuous granular fractions with larger particle sizes.
2. Content of needle and flake particles
The content of needle and flake particles in crushed stones or pebbles should meet the requirements of:
· 3. Mud content

For concrete with frost resistance, impermeability or other special requirements, the mud content in the gravel or pebbles used should not exceed 1.0%. When the mud content of gravel or pebbles is non-clay stone powder, the mud content can be increased from 0.5%, 1.0%, and 2.0% in the above table to 1.0%, 1.5%, and 3.0% respectively.
· 4. Mud content

For concrete with a strength grade less than C30 that has frost resistance, impermeability or other special requirements, the content of gravel or pebble mud should not exceed 0.5%.
· 5. Gravel strength
The strength of gravel can be expressed by rock compressive strength and crushing value indicators.
When the concrete strength grade is greater than or equal to C60, rock compressive strength testing should be carried out. The crushing value indicators of gravel and pebbles are as follows:
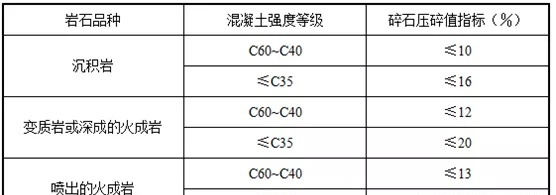
Note:Sedimentary rocks include limestone, sandstone, etc.; metamorphic rocks include gneiss, quartzite, etc.; plutonic igneous rocks include granite, syenite, diorite and peridotite, etc.; extrusive igneous rocks include basalt and diabase..
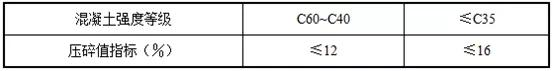
· 6. Robustness
The solidity of gravel or pebbles should be tested by the sodium sulfate solution method, and the mass loss should comply with the requirements in the table below.

· 7. Apparent density & continuously graded loose packing void ratio
The apparent density of gravel or pebbles should not be less than 2600kg/m3. The void ratio of continuously graded loose accumulation should comply with the following table:

· 8. Water absorption rate

· 9. Content of harmful substances
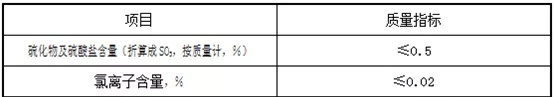
· 10. Alkali activity test
For important structural concrete that has been in a humid environment for a long time, the gravel or pebbles used should be tested for alkali activity. When conducting alkali activity testing, the petrographic method should first be used to test the variety, type and quantity of alkali active aggregates. When it is detected that the aggregate contains potential alkali silicic acid reaction, the rapid mortar rod method, mortar length method or concrete prism method should be used to test the alkali activity; when it is detected that the aggregate contains active alkali salts, the rock should be used Column method for alkali activity testing.
When it is judged through alkali activity testing that there is a potential alkali-silicic acid reaction hazard, the alkali content in the concrete should be controlled not to exceed 3kg/m3, or effective measures to inhibit alkali-aggregate reactions should be taken; there is a potential alkali-carbonate reaction When hazardous, it should not be used as concrete aggregate. Otherwise, special concrete tests should be passed for final evaluation.
 選擇語言
選擇語言















 Home
Home Product
Product Telephone
Telephone Message
Message